
The AR days formula is valuable for healthcare businesses because it calculates the average number of days it takes to receive reimbursement.
Practices that are not involved in regular AR days calculations result in revenue loss, delayed payments and unsatisfied patients.
Hence, to enhance your business’s revenue efficiency, get deeper knowledge of AR days, the a/r days formula, and the simplified AR process in medical billing.
The AR full form in medical billing is accounts receivable. It refers to the money owed by payers and patients to the healthcare provider for rendered services. The most popular AR amounts included in billing are:
An AR days calculation metric is important in medical billing because it indicates a practice’s financial health and ability to generate revenue.
AR days, also known as Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) or Debtor Days, are a key financial metric indicating how efficiently a business manages its revenue. Despite their many names, they measure the average time it takes to convert receivables into cash.
In other words, if DSO time is low, it means the client pays on time, and the company’s cash flow is strong. However, if days in accounts receivable get longer, payment collection is delayed, which increases the financial pressure on the business.
AR days calculation is important for a healthcare business to analyze the cash flow and financial health. Practices that want to calculate AR days need to follow an AR process in medical billing, which includes:
Learn what a/r days show. Generally, it means the average number of days it takes for your company to collect payment after issuing an invoice. Lower days mean higher reimbursement, while longer days mean financial pressure.
Collect key financial metrics to understand the business’s financial track. These include.
Ensure the accounts receivable and credit sales are gathered within the same time frame. For instance, both are gathered from the past 12 months.
After you’ve collected the data and the timeframe, you can calculate it using the standard a/r days formula.
The AR days formula is a financial mapping metric in medical billing that shows how long it takes a practice to collect revenue from a patient or insurer after delivering service. It helps measure the efficiency of the revenue cycle. The standard formula for days in AR calculation for healthcare is:
AR Days = Total Accounts Receivable ÷ Average Daily Charges
Here’s an example showing how to calculate AR days in medical billing. Imagine a clinic with $90,000 in accounts receivable and $270,000 in billed amounts over the past 90 days. The average daily charges would be 3,000$ as by ($270,000 ÷ 90). Now, by using the AR days formula in medical billing.
AR days = $90,000 ÷ $3,000 = 30 days
This means the clinic typically takes 30 days on average to receive payment for a service delivered. The ratio below 40 days means the practice’s revenue cycle efficacy is good, and it maintains a steady cash flow and financial health.
Longer a/r days impact the healthcare reimbursement process by disturbing the cash flow, increasing the risk of bad debt, and through negative financial metrics. Here’s the detailed elaboration of deeper impacts.
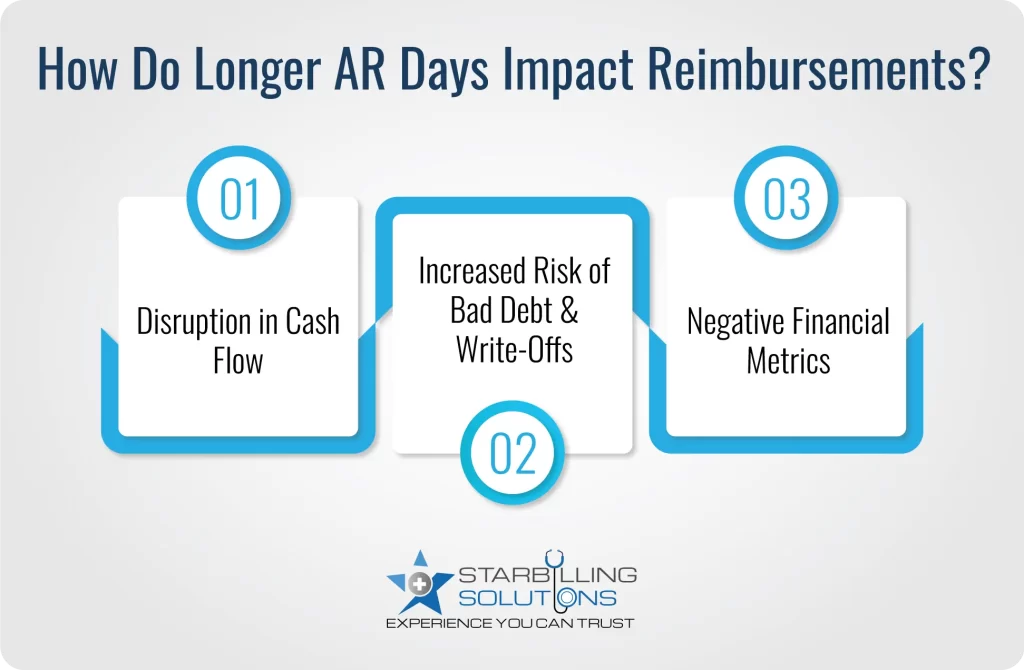
When longer days in ar are common, many practices feel intricate in covering operational costs such as salaries, rent, equipment and vendor payments. This leads them to rely on credit and emergency funds to get on track in business, ultimately pushing the practices to financial stress, and reducing the investment in business growth.
The longer the claim or patient balance goes unpaid, the greater the chances of practices being written off as bad debt. In other words, the unpaid payments for 90 to 120 days ruin profitability and increase the administrative burden through unnecessary collections.
Longer days in accounts receivable result in slowed reimbursement, making it harder for providers to achieve a sustainable profit margin. The negative financial metric leads to businesses being stuck in revenue growth and lower patient satisfaction.
A company’s receivables, which represent money owed by its customers for goods or services, increase the AR days due to various factors. These include denied claims, lack of AR audits, and slowed insurance payments.

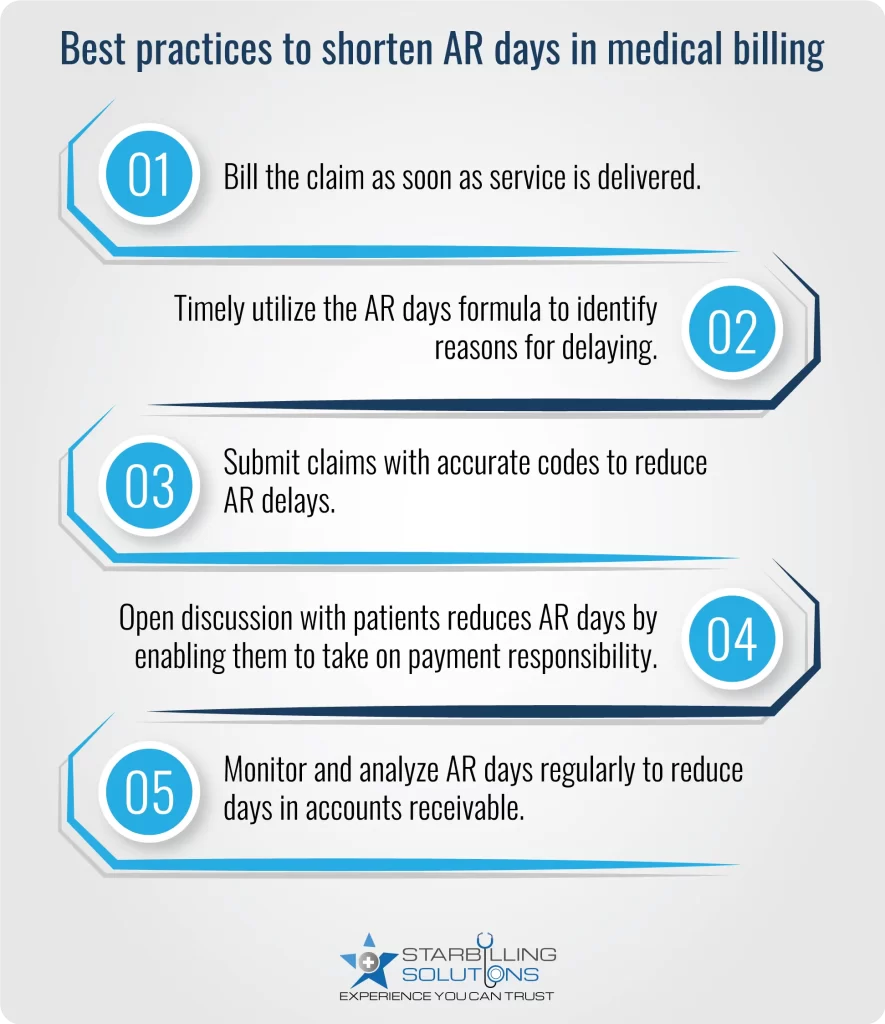
If a practice misses the regular accounts receivable days calculation audits, it may result in missing priority claims and unresolved denials. This means the old claims may go unnoticed, which consistently increases AR days and delayed collections.
When patients are not reminded in time about their unpaid balance, the payment process may take weeks or months. High out-of-pocket costs or unclear billing statements are common reasons why patients refuse to pay their portion of the payment, increasing the days in accounts receivable healthcare.
Claim errors, such as coding errors, missing information or eligibility issues, lead to denials. As the claim denials are repeated, more days are added to the correction process, ultimately adding more days to AR.
Even when a claim is processed without error, many insurance companies still take weeks or months to reimburse the provider. This kind of payment delay is not in the provider’s control, but it still affects the AR days in medical billing.
Best practices such as clear claims, timely billing, and better payer negotiations could reduce the AR days and improve the healthcare revenue cycle. Here are the key points to follow to shorten days in AR.
Longer AR days could slow down your practices from achieving the desired revenue. Resultantly, you could end up with budgeting problems and an unsatisfactory patient experience. Hence, to streamline your practice’s accounts receivable, hire our AR expert billers.With our team offering expertise in AR days formula and payment analysis, we identify the pain points and allow targeted action that shortens a/r days and boosts cash flow. So why delay? Consult Star Billing Solution today and accelerate collections, improve financial visibility, and keep your practice financially healthy.