
Health care reimbursement takes the central place when it comes to boosting revenue cycle management for your practices. Faster reimbursement helps practices become financially healthy while ensuring patients get premium care. However, with the changing world of healthcare reimbursement in medical billing, staying at the top of other businesses isn’t just optional, but it’s necessary. That’s why you need this comprehensive guide to optimize reimbursement for your clinic or hospital.
Are you eager to know what reimbursement in Healthcare is? In simple terms, healthcare reimbursement is the money paid back to the provider after a medical service is rendered to the patient. Sometimes, patients reimburse the clinic out of pocket if they are not registered with any insurance company.
But mostly, instead of paying out of pocket, the patients opted to contact their insurance provider (private, public, or employer insurance) to pay on their behalf. Although healthcare reimbursement systems vary based on payers and policies, the aim is to provide timely and accurate payments.
key Terms
In today’s healthcare business, reimbursement for hospitals and clinics is important because it assists doctors in getting paid for offered services. Many reasons why it is important in 2025.
Healthcare providers need adequate reimbursement from insurance companies, government programs (Medicare/Medicaid), and patients to cover hospital expenses. This way, they can cover staff salaries, upgrade practice equipment, and pay for technology and billing software or services. If they face ample reimbursement delays, they can’t operate properly and sustainably.
If the providers get health care reimbursement on time, there is a greater chance that they will accept more insurance plans and may expand their offered services for a better patient experience. Moreover, they could invest in providing facilities and equipment. Doing so makes it easier for patients to find quality care in unserved areas.
Healthcare providers can plan their financial activities more effectively when they get timely and accurate billing and reimbursement. They could forecast revenue, plan budgets for new hires, or even they could spend more on training new staff and development. This keeps the entire healthcare system balanced and functional.
Learning the insurance reimbursement process in healthcare is essential to ensure fair compensation for patient services. Here’s a detailed breakdown showing how is a health provider reimbursed by an insurance provider
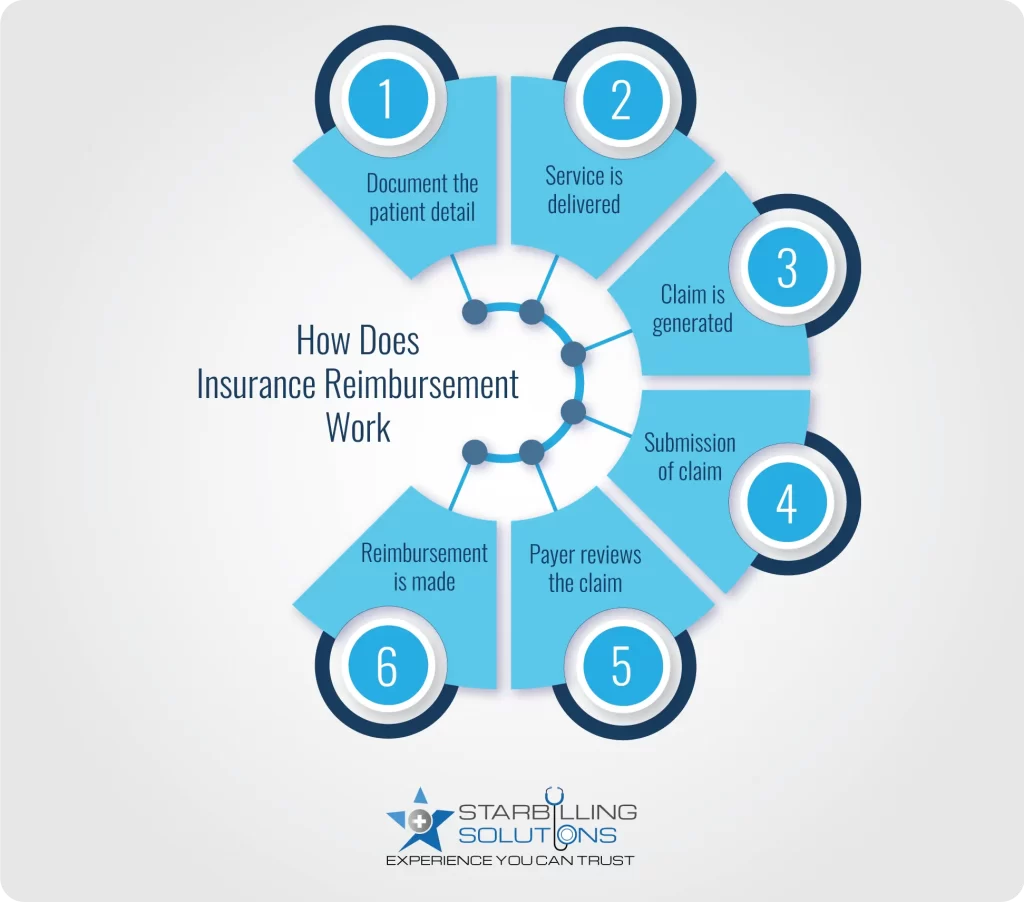
Healthcare reimbursement in medical billing starts with gathering patient information, including their name, contact details, and insurance information. Providers then analyze the diagnosis and create a treatment plan.
Based on the plan, the doctor performs treatment and notes down the CPT and ICD-10 codes and how much the insurer needs to reimburse them. This is important because sometimes the patient pays some amount out of their pocket, and the insurance company needs to reimburse the rest.
A detailed health insurance claim reimbursement is now generated by the provider’s end, which enlists the patient’s details, service details, and lastly, the clinic or hospital information. The codes are reviewed again so there are no errors in claims, leading to denial cases.
It’s time to submit the claim for a quick payer reimbursement and boost revenue cycle management healthcare. In-network providers are registered with companies, so they submit claims on their own. However, if a hospital or clinic operates as an out-of-network provider, they hand over a superbill to the patient, and they submit it to the payer by themselves.
The insurance company has an in-house team that cross-checked the claim details. They review the patient’s information and check if he/she is eligible for the service he rendered at the hospital. Then, they check the codes and ensure accuracy. Lastly, they verify the provider’s details to see whether the amount they ask for billing and reimbursement is valid.
In the approval state, the insurance company releases the payment to the provider for the service they delivered to the patient. The healthcare provider can challenge the reimbursement for hospitals if the payer has not delivered the expected amount. However, the healthcare reimbursement in medical billing could take a few weeks to a few months, depending on the insurance company’s policies.
The most common healthcare payment models include fee-for-service (FFS), capitation, global, bundled, and cost-based models. Each model takes a unique approach to reimbursing healthcare providers. Below is a detailed definition along with the pros and cons for each.
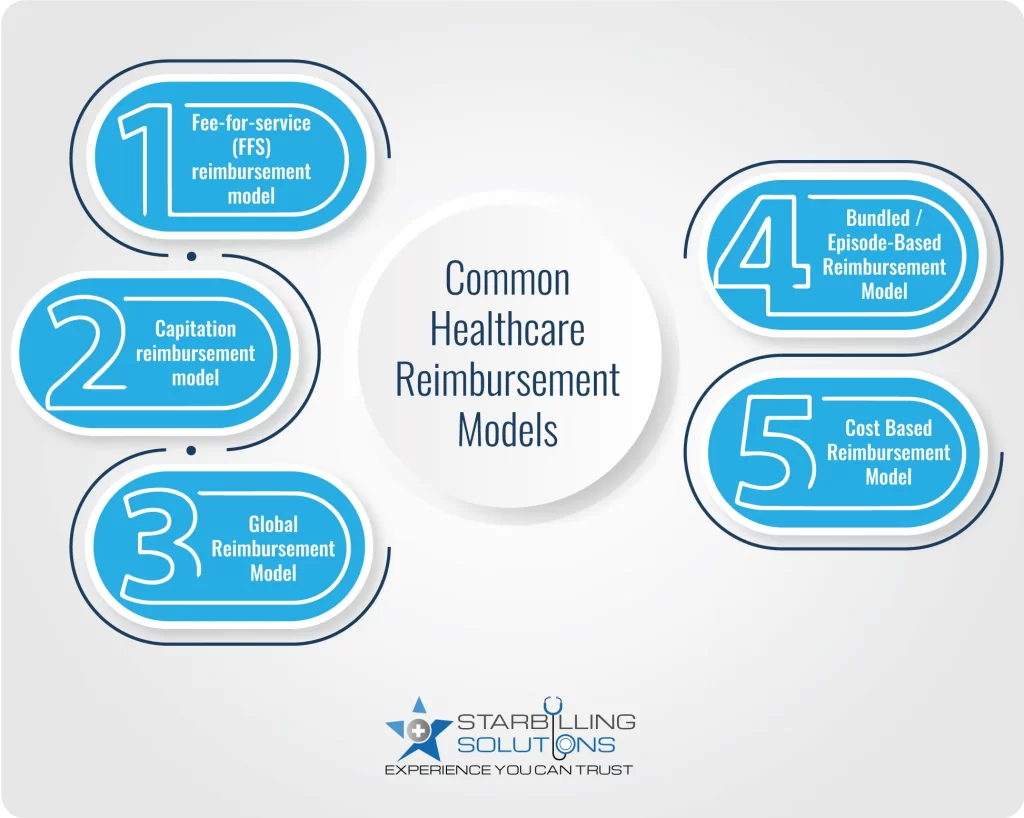
This is one of the most traditional healthcare payment models, where the provider gets reimbursed for each individual service. Let’s say a patient visits a doctor with knee pain. The doctor examines it; that’s the one fee. Now, the doctor asks for an X-ray; that’s another fee. The doctor gives a knee pad, which costs additionally. So, you get three services, and you pay for each one.
| Pros | Cons |
| Easy to understand and implement | Leads to unnecessary procedures |
| Clear and transparent billing process | Focus more on quantity than quality of services |
| Flexible across all specialities | Time-consuming, as each service needs individual claim submission |
What is capitation reimbursement? It is one of the types of reimbursement models in which insurers pay a fixed amount to a provider regardless of how much care the patient receives each month. Capitation reimbursement is far better than other models because providers get paid without delivering claims daily. Also, they get paid every month, which ensures they can process staff salaries and facility bills in a timely manner.
| Pros | Cons |
| More predictable healthcare costs | The provider bears the expense if the cost of care exceeds the monthly charges |
| Capitation reduces the administrative burden and the billing process | Capitation leads to lower quality care and patient satisfaction |
Global health care reimbursement is a model in which doctors are paid for a group of services at once instead of individually for each service. Take ankle surgery as an example, where a patient gets an initial visit, surgery, and follow-up guidance for months, all services combined in a package. Now, the doctor will bill the claim to a healthcare reimbursement systems and get paid a global fee.
| Pros | Cons |
| Streamline billing and reduce admin work | Not a right fit for all types of medical care |
| One bill submission and more significant pay return | It’s hard to predict all treatment needs upfront |
| Encourage collaboration among providers | Requires high transparency in care delivery |
Very similar to global reimbursement methodologies, where the provider covers multiple services for extended periods, the bundled reimbursement model offers a single predetermined payment that covers all services under a patient’s one episode of care, which is condition-specific and time-bound. Let’s say a patient had heart surgery under a bundled reimbursement plan. The hospital surgeons and faculty receive one payment, which includes surgery payment and post-90-day observation and treatment.
| Pros | Cons |
| Encourage collaboration among different providers to enhance care management. | This model is complex to implement and manage. |
| Aligns providers’ incentives for cost-effective quality care | Providers face financial loss if patient care costs exceed. |
In a cost based reimbursement model, providers are paid based on actual costs incurred during patient care. Let’s say a hospital spends 1 million dollars annually on nurses, doctors, facilities, and extra bills. They prepare and audit reports and submit Medicaid, showing total expenses. They audit the report, and if justified, they agree to reimburse enough to support the clinic’s ability to keep its doors open for patients. This reimbursement methods in healthcare is most widely used in critical access hospitals or rural settings.
| Pros | Cons |
| Reduce financial risk for providers | A comprehensive audit-ready process |
| Encourage access to premium care in underserved areas | Low financial benefits for the provider as health reimbursement happens on actual spent cost |
Widely seen reimbursement risk include:
These challenges for reimbursement in medical billing lead to payment delays, loss of revenue, and extra administrative burdens. Additionally, the organization’s services and resources suffer, and patients receive worse services every day. In the long run, it will negatively impact the organization’s reputation, causing staff to leave for good.
Ultimately, these risks lead the provider to burn out. Therefore, develop effective billing strategies and steer these challenges to sustain a healthy cash flow and quicker, yet accurate medical reimbursement.
The annual growth rate of healthcare reimbursement is 17.3%, from $13.41 billion in 2024 to $15.73 billion in 2025, and it is expected to grow even more in the next few years. These stats show how essential it is to adopt new reimbursement strategies to capture the maximum revenue. So, without further delay, let’s review some top strategies to optimize healthcare reimbursement solutions.
Are you tired of endless claim denials and too many payment delays? Now is the right time to take control of healthcare reimbursement management. At Star Billing Solutions, we help healthcare providers streamline the billing cycle and get reimbursed quickly and accurately. Our healthcare reimbursement services are planned to reduce administrative burden, minimize errors, and guarantee claim approval over 90%. So, while we collect money behind your back, you focus on quality patient care.
Sum up all the eligible medical expenses for the given services. Then, determine how much the insurer paid for each expense, side by side, considering the deductible, copay, and coinsurance. Now, subtract the amount your insurance paid from the total medical expenses. The remaining amount is what you get reimbursed for.
Out-of-pocket payment: Patients don’t have insurance coverage, so they must pay the entire amount out of their own pocket.
Individual private insurance: Individuals buy healthcare insurance directly from private insurers on their own or through a marketplace like ACT.
Employment-based private insurance: Many employers offer their employees short- and long-term health insurance coverage.
Government financing: Public programs fund healthcare insurance, such as Medicare for the elderly and disabled, and Medicaid for low-income persons.
Fee for service (FFS) is the standard healthcare reimbursement method in which doctors get paid for every service they deliver to patients, whether it's just a visit, test, or detailed procedure. The more patients get visits, the more payment doctors collect. On the other hand, in capitation, the doctor receives a fixed amount per patient per month, regardless of how many services the patients receive.
Inpatient services: Medicare pays hospitals using the inpatient prospective payment system (IPPS). In simple terms, the hospitals get reimbursed a fixed amount based on diagnosis-related groups (DRG), regardless of the total service cost.
Physician services: Medicare pays doctors using the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule. Payouts are based on Relative Value Units (RVUs) assigned to services, which are adjusted for geographic factors and a conversion factor.
In the context of medical billing, coverage refers to services and procedures the insurance company agrees to cover. On the other hand, healthcare reimbursement is the actual amount that the payer delivers for those covered services.