
An offset in medical billing comes to actions when a payer delivers an excess amount of payment to the provider for rendered services. In this situation, a payer may adjust the payment for the upcoming claim or issue a refund notice to the provider.
If offsetting is not managed efficiently, it could result in compliance risk, affecting cash flow, or confusion in payment reconciliation. Therefore, we craft this article, enlisting everything, including overpayments, offsets, refunds, recoupments, and how to effectively manage them.
To streamline practice’s revenue efficiency, providers should ensure they maintain a consistent flow of payment for each service rendered. And to do this, they have to understand the key term related to offset in medical billing.
An overpayment is a key term in medical billing where a healthcare provider receives more reimbursement from a payer than what is actually due. Let’s say a payer is responsible for delivering 70$ to the provider, and he unintentionally transferred 90$. Now the excessive 20$ is known as overpayment.
The offset meaning in medical billing indicates a process where a payer deducts the previously overpaid amount from the provider’s future payments. In other words, instead of requesting the provider to pay back the excessive amount, the payer applies the owed amount as a credit and deducts it from the next claim.
Refund in medical billing is when the healthcare provider returns the excessive payment to the payer, whether voluntarily or by demand, through an overpayment notice. This form has an accounts receivable number (AR#), which identifies the payment. If the payer doesn’t receive the refund after 30 days, they can reprocess the notice, and after 40 days, the provider will be charged an interest rate.
Recoupment meaning in medical billing, is to offer the payer legal rights to recover an overpaid amount from the provider. The payer initiates the recoupment process to reclaim the excess funds through a direct refund request or an offset from future payments.
Recoupment and offset payment in medical billing are both mechanisms used alternately because they both allow insurance companies to adjust overpayments. However, there are some differences in their purpose, application and timing.
| Aspects | Offset | Recoupment |
| Purpose | It adjusts the current payment on the basis of past overpayment. | It recovers the overpayment typically when the payer has already paid the claim. |
| Application | The insurer deducts the overpaid amount from the current claim payment. | The insurer requests a notice for recovering overpayment or deducting from future payments. |
| Timing | The correct time for the offset is when a new claim is processed. | The correct time for recoupment is when the payer has already paid the claim and identifies overpayment later. |
To get a deeper understanding of offset in medical billing, we are going to offer a real-life example. Let’s say a therapy clinic delivers you a physical therapy session costing 100$. Patients pay the 30$ out of pocket while the remaining 70$ is the payer’s responsibility.
But unfortunately, due to some medical insurance eligibility verification problem or delays in revenue recognition, the payer delivers the 90$. Now, instead of requesting the clinic, the payers applied an offset. Next time, the same provider has updated the claim of 150$ to the payer, but the payer issued 130$ because the provider owed the previous 20$.
However, if the provider has returned the 20$ at the time when the payer has requested through a notice, then it will be marked as a refund. Ultimately, the recovery of the funds would require formal steps from the payer, which would be considered recoupment.
An offset in medical billing occurs when payers pay the provider more than they owe. In billing, this is essential to eliminate any financial loss. However, some major causes that lead to offset are described below.

Offsets occur sometimes because the insurance company pays the provider more than what they owe. It is often caused by claim processing errors, duplicate payments, or system glitches.
The provider often agreed upon a middle payment agreement with the insurance company. But at the time of billing, the provider may charge more than the agreed-upon fee for the service. In such a condition, the offset occurs to balance the payment in future claims.
Common coding errors, such as inaccurate POS codes and ICT, CPT codes, are quite common in medical billing, which leads the insurance company to pay a higher amount. For example, a coding error could indicate a wrong service, which has higher reimbursement charges than the actual service you delivered. Under such circumstances, payers call for an offset payment in medical billing.
If a patient pays a copay or deductible upfront, which the insurance company also covers in reimbursement, leading to an amount paid maximum than owed. This will also require the adjustment via offset.
Sometimes, service claims are reimbursed on the first attempt, but later, the payer does an audit, which shows the provider is overpaid for the rendered service. Then, offsets are applied to future claims to reconcile the balance.
Offset in medical billing plays a critical role in managing the healthcare revenue cycle of healthcare providers. However, some unconditional causes lead to offset, and the provider experiences the consequences, including payment shortages, delays in revenue, and administrative burdens.
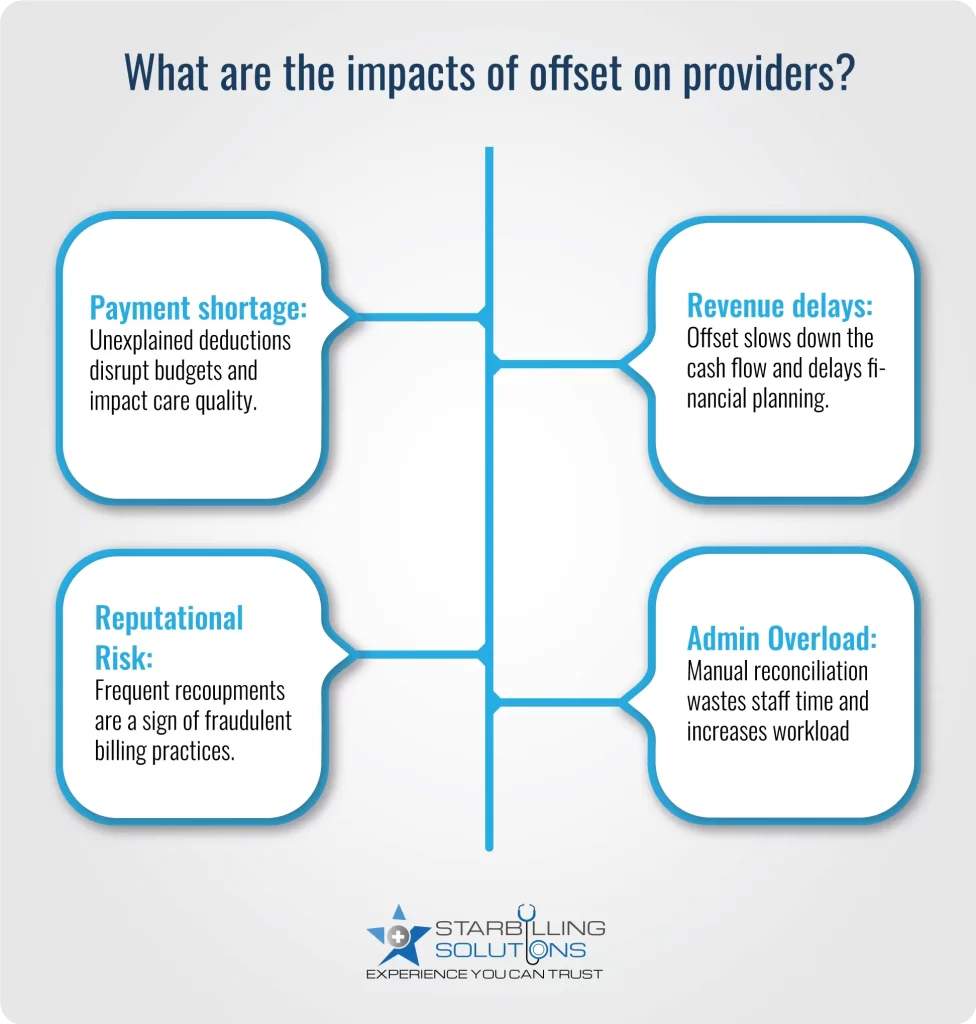
Sometimes, providers need reimbursement amounts to update facility equipment or salaries. In such a critical time, insurance companies deduct the payment to balance the overpayment. This unexplained payment shortage leads to confusion in the revenue gap and affects the quality of healthcare.
When payers pose an offset payment in medical billing against previous credit or overpayment, the current service revenue is deducted or delayed. This deduction in revenue affects the cash flow and financial forecasting
Repeatedly occurring recoupments are not a good sign for your healthcare. It leaves a bad impression on payers and patients that your practice is engaging in fraudulent billing activities like overbilling, upcoding, and unbundling to get higher reimbursements.
Reconciling the offset needs some manual effort. For instance, the staff must match and investigate the payment with the offset, which often requires maintaining contact with both payers and patients. This diverts more time and resources from actual administrative duties, increasing the staff overhead burden.
At Star Billing Solutions, we understand how offset affects your cash flow and burdens your staff with administrative work. That’s why we offer a strategic approach and key steps to prevent and manage offsets effectively.
Overall, we understand the common causes and impacts of offset in medical billing and implement best practices to manage and prevent them. By working with our expert team, your practices can improve their billing processes and overall patient satisfaction.